Blood pressure is a critical indicator of your overall health, and understanding your blood pressure readings is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly half of adults in the United States (48.1% or 119.9 million) have hypertension. Blood pressure measurements determine the force of blood against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood throughout your body. This guide will delve into the significance of these readings, how they are measured, and what they mean for your health.
What Is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. It is a principal vital sign and a crucial indicator of your circulatory system's health. Blood pressure is expressed in terms of systolic and diastolic pressure.
- Systolic Pressure: This is the higher number in a blood pressure reading, indicating the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats and fills them with blood.
- Diastolic Pressure: The lower number represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats.
Your blood pressure is typically recorded as two numbers separated by a slash, for example, 120/80 mmHg. The first number (systolic) represents the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats. The second number (diastolic) indicates the pressure between heartbeats. "mmHg" stands for millimeters of mercury, the unit used to measure blood pressure.
Blood pressure readings are categorized into several ranges to help identify potential health issues:
- Normal Blood Pressure: A reading below 120/80 mmHg is normal. This range indicates that your heart and arteries are working efficiently to pump and receive blood.
- Elevated Blood Pressure: A systolic number between 120 and 129 mmHg and a diastolic number below 80 mmHg is an indicator of elevated levels. It suggests that you may be at risk of developing high blood pressure unless steps are taken to control it.
- Hypertension Stage 1: When your systolic pressure is between 130 and 139 mmHg or your diastolic pressure is between 80 and 89 mmHg, you're considered to have stage 1 hypertension. This stage often requires lifestyle changes and possibly medication to manage blood pressure.
- Hypertension Stage 2: This is a more severe form of high blood pressure, with systolic readings of 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic readings of 90 mmHg or higher. Treatment often includes a combination of medications and significant lifestyle adjustments.
- Hypertensive Crisis: A systolic reading above 180 mmHg or a diastolic reading above 120 mmHg is a medical emergency. Immediate medical attention is required as this can lead to heart attack, stroke, or other critical conditions.
Factors Influencing Blood Pressure
Several factors can affect blood pressure readings, making them fluctuate throughout the day:
- Physical Activity: Blood pressure typically rises during physical activity and falls during rest.
- Stress: Emotional stress and anxiety can temporarily increase blood pressure.
- Diet: High salt intake, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of essential nutrients can elevate blood pressure.
- Medications: Certain medications, including over-the-counter drugs like NSAIDs and some prescriptions, can raise blood pressure.
- Health Conditions: Kidney disease, thyroid problems, and sleep apnea can influence blood pressure.
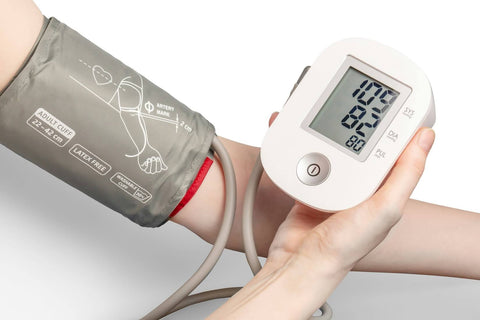
How To Measure Blood Pressure Accurately
To get an accurate blood pressure reading, follow these guidelines:
- Prepare Properly: Avoid caffeine, smoking, and exercise for at least 30 minutes before measuring. Ensure you have rested for at least 5 minutes in a calm environment.
- Position Correctly: Sit with your back straight and supported, feet flat on the floor, and your arm supported at heart level.
- Use the Right Equipment: A properly calibrated and fitting blood pressure cuff is crucial. Ensure it is placed snugly around the upper arm, just above the elbow.
Lifestyle Changes To Manage Blood Pressure
Managing blood pressure often involves making lifestyle adjustments, such as:
- Healthy Diet: Adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is designed to help lower blood pressure.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming. A study in the Journal of Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology found that regular moderate to vigorous physical activity can lower blood pressure by an average of 5-7 mmHg.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce blood pressure.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Both smoking and excessive alcohol can raise blood pressure. Reducing alcohol intake and quitting smoking can have immediate benefits.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and regular relaxation can help lower stress and, consequently, blood pressure.
When to See a Doctor
Regular monitoring is key to managing blood pressure effectively. See a doctor if:
- You consistently get readings in the hypertension range.
- You experience symptoms of a hypertensive crisis, such as severe headaches, chest pain, or difficulty breathing.
- Your blood pressure medication doesn’t seem to control your hypertension effectively.
Take Control of Your Blood Pressure: Next Steps for Healthier Living
Understanding your blood pressure readings is crucial for early detection and management of potential health issues. By keeping track of your readings and recognizing the factors that influence them, you can take the next step toward improving and maintaining your cardiovascular health.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial for monitoring blood pressure and overall health. Additionally, adopting healthy lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can significantly impact blood pressure levels. If necessary, your doctor may recommend additional medical interventions to ensure your blood pressure remains in a healthy range.
For those seeking a natural approach to managing their blood pressure, PhytAge Laboratories offers Blood Pressure 911, a unique supplement designed to support cardiovascular health.
Blood Pressure 911 combines key nutrients and herbal extracts known to help regulate blood pressure and improve heart function. With ingredients carefully selected for their efficacy and safety, Blood Pressure 911 is an excellent choice for anyone looking to complement their health routine with a high-quality, natural solution. Contact us today to explore how Blood Pressure 911 can be part of your journey toward optimal blood pressure and enhanced heart health today.

 Cart
Cart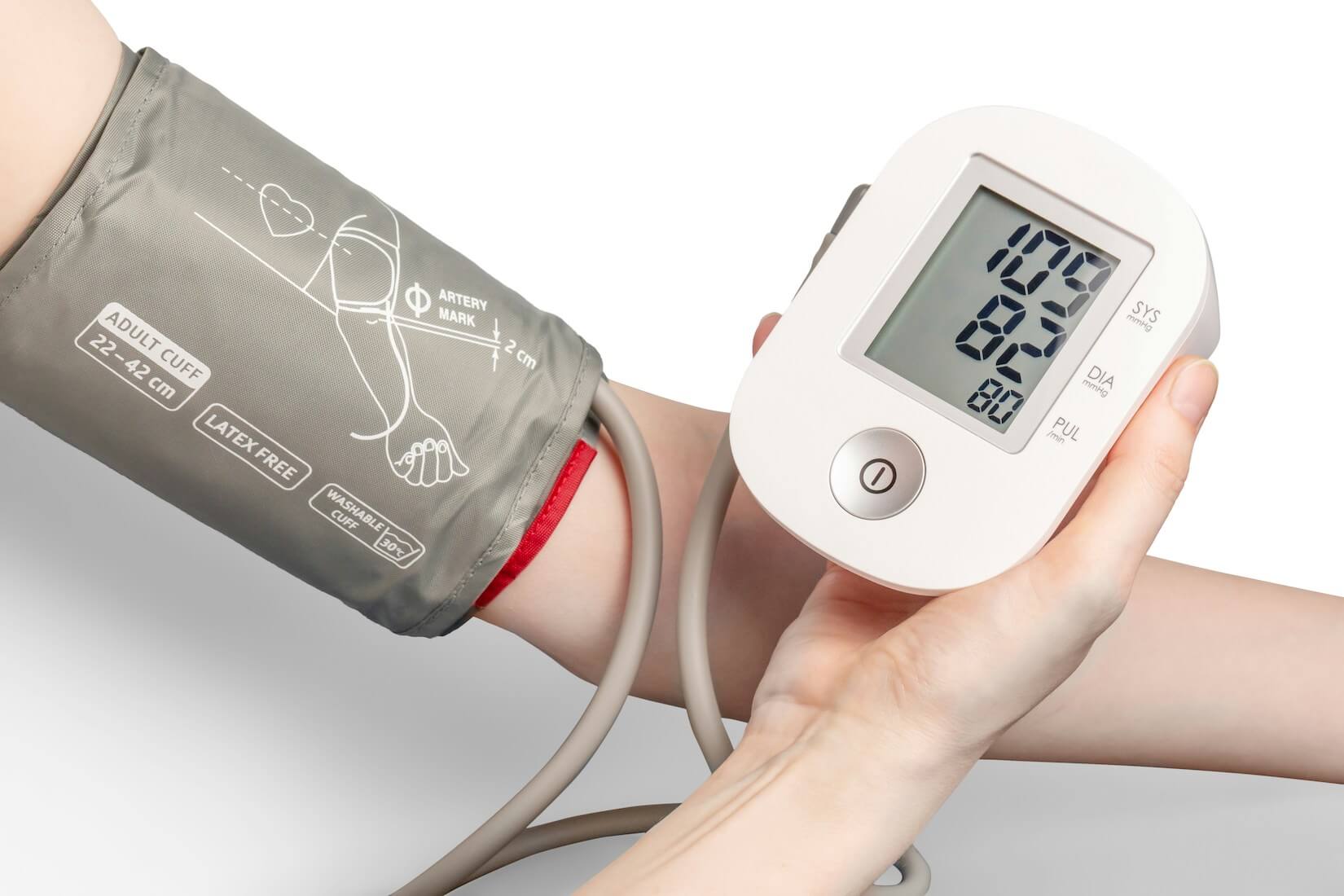













































 1-800-822-5753
1-800-822-5753
