Over 75% of Americans use dietary supplements, with the vast majority being in the form of capsule pills. Capsule pills represent one of the most common and preferred dosage forms for medication delivery. Their popularity stems from several advantages, including ease of ingestion, precise dosage, and the ability to mask unpleasant tastes and odors of the medication contained within. But have you ever wondered what the shell of a capsule pill is made of? Let's explore the materials that comprise capsule shells and their significance in drug formulation.
The Two Main Types of Capsules
Capsule shells can be broadly categorized into two types: hard-shelled and soft-shelled. Hard-shelled capsules are typically used to contain dry, powdered ingredients or miniature pellets. In contrast, soft-shelled capsules are used for oils and for active ingredients that are dissolved or suspended in oil.
Hard-shelled Capsules: Composition and Characteristics
Hard-shelled capsules are made from gelatin or a gelatin substitute such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) for vegetarians or those with dietary restrictions that preclude gelatin consumption. Gelatin, derived from collagen obtained from various animal by-products, has been the traditional choice for many years. It offers excellent biocompatibility and is generally recognized as safe by regulatory authorities worldwide.
HPMC, on the other hand, is a form of cellulose, a plant fiber. This material is particularly favored for its vegetarian origin, providing an alternative for those who avoid animal products. HPMC capsules are also known for their stability over a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for products that require heat in their manufacturing process or are distributed in hot climates.
Soft-shelled Capsules: Composition and Characteristics
Soft-shelled capsules, also known as softgels, are made from gelatin mixed with plasticizers such as glycerin or sorbitol to make the shell soft and flexible. Like hard-shelled capsules, softgels can encapsulate ingredients in liquid form, including oil-based solutions and suspensions. The gelatin mixture is spread on a flat surface to form two sheets, which are then wrapped around the liquid medication to create a sealed capsule. This method is particularly useful for oils, fat-soluble vitamins, and other substances that are liquid at room temperature.
Advancements in Capsule Materials: Vegan and Hypoallergenic Options
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for vegan and hypoallergenic capsule options. This demand has led to the development of new materials for capsule shells, such as pullulan. Pullulan is a polysaccharide polymer derived from the fermentation of tapioca or corn. It is entirely plant-based and offers an excellent alternative for those seeking vegan medication options. Pullulan capsules are known for their natural origin, excellent oxygen barrier properties, and being environmentally friendly.
The Role of Capsule Shells in Drug Delivery
The material of the capsule shell plays a critical role in the drug delivery process. It protects the active ingredients from degradation and can influence the rate and extent of drug release. For instance, certain modifications to the gelatin or HPMC formula can create capsules designed to dissolve at different rates, allowing for immediate release, delayed release, or sustained release of the medication into the bloodstream.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
The safety of capsule materials is of paramount importance. Gelatin, HPMC, and pullulan have all been extensively tested for safety and are approved by regulatory authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), for use in pharmaceutical applications. Manufacturers must adhere to strict quality control standards to ensure that the capsules do not interact with the contained medications in a way that could alter their efficacy or safety.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of capsule production is another consideration. Gelatin capsules, derived from animal by-products, raise concerns regarding sustainability and animal welfare. In contrast, plant-based capsules, such as those made from HPMC or pullulan, are considered more environmentally friendly due to their renewable sources and the absence of animal-derived ingredients.
The Future of Capsule Technology
The field of capsule technology continues to evolve, with ongoing research into new materials and formulations to enhance drug delivery, patient compliance, and environmental sustainability. Innovations such as capsules that can deliver multiple drugs at different rates or capsules that can withstand the harsh environment of the stomach to deliver drugs directly to the intestines are on the horizon.
The Future of Medicine Delivery
The shell of a capsule pill, whether made from gelatin, HPMC, pullulan, or other materials, is a critical component of modern pharmaceuticals, offering a versatile and effective means of medication delivery. As technology advances and consumer preferences evolve, we expect further innovations in capsule composition and functionality in the future. The development of safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly capsule materials will continue to play a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry, ultimately benefiting patients worldwide.
Understanding the materials that make up the capsules we take is fascinating and essential for those with specific dietary restrictions, allergies, or concerns about the environmental impact of their medication choices. As we look toward the future of pharmaceuticals and the ongoing innovations in capsule technology, it's essential to recognize the contributions of pioneers in the field, such as PhytAge.
PhytAge is at the forefront of developing advanced health solutions that cater to the evolving needs and preferences of consumers, ensuring that efficacy, safety, and sustainability are at the heart of their products. Explore PhytAge’s range of innovative health solutions today and take a step towards embracing cutting-edge advancements in capsule technology.

 Cart
Cart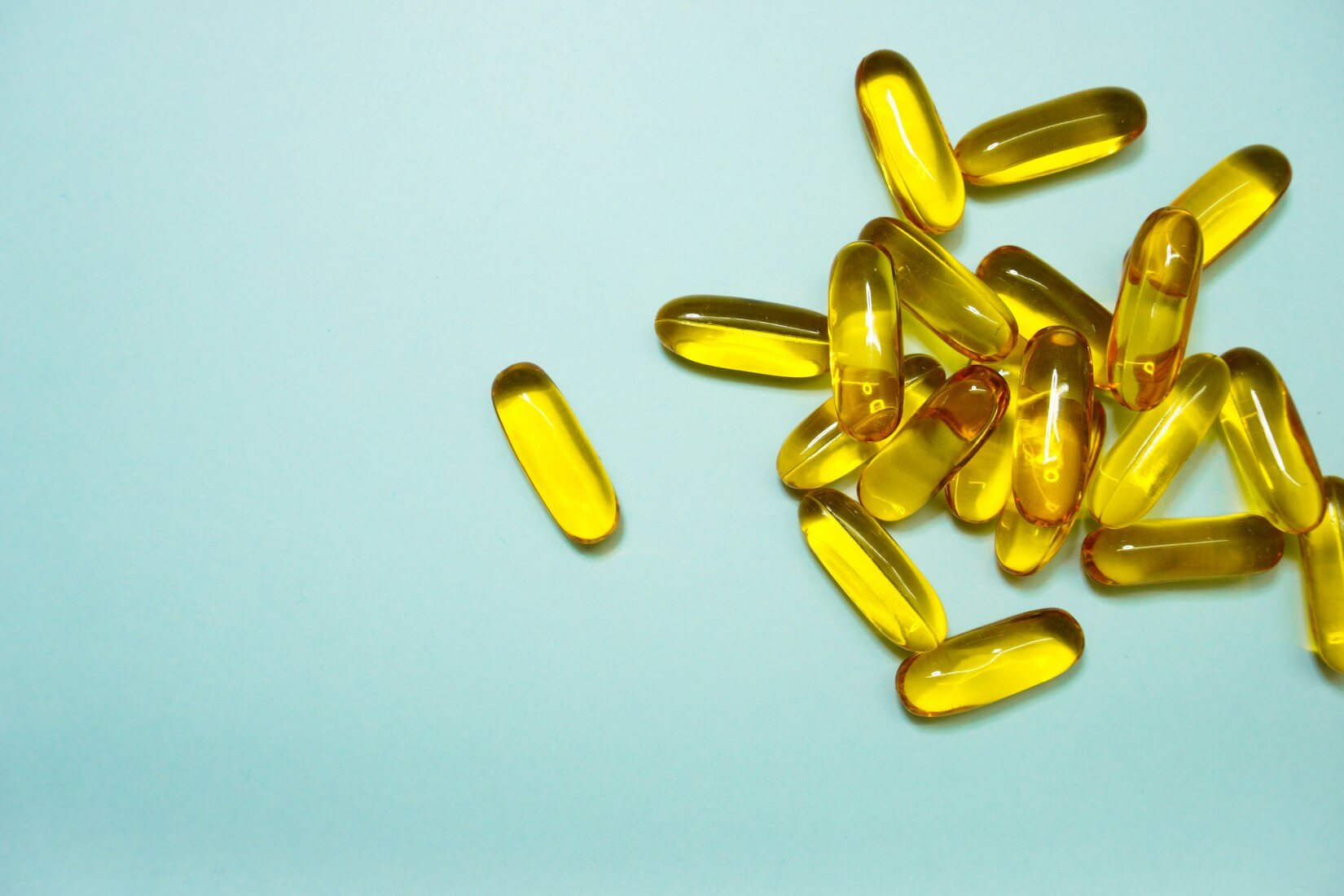












































 1-800-822-5753
1-800-822-5753
